8 Must-Have Cybersecurity Solutions for Your Protection
The eight cybersecurity solutions I have listed below can be lifesavers from time to time. Although they may be static and old school, they are still worth using for cybersecurity. They will prevent 90% of current vulnerabilities and while they may make your life difficult, you will also benefit a lot.
1.VPN (IPsec, L2TP, openvpn, EVPN) and 2FA
To monitor people, gain access, and identify access constraints, you need to connect them with an isolated tunnel. For this purpose, your setups must have VPN and 2FA.
2.Firewalls are not a load-balancer
Using extra features on firewalls mostly creates problems for you. Most of these features are put up for bidding and marketing. Enabling such features on a firewall can make you susceptible to DDOS and WAF attacks. People who test the system’s weaknesses understand that the firewall’s CPU creates 100% load when WAF is used to make three complicated requests.
3.Single-purpose servers
Instead of a single server for multi-purposed services, use different servers that provide only certain services. For example, do not use mail servers to share a file, or do not host your website on a LAMP Server.
If you do this, you will create a severe impact area. At the end of the day, a security breach in one stack will affect your other stacks. You will be creating hotspots with your hands. The graphic below shows tools that can be applied from the most secure architecture to a less secure one. The security gap that may occur on the LAMP server will provide access to the whole system.
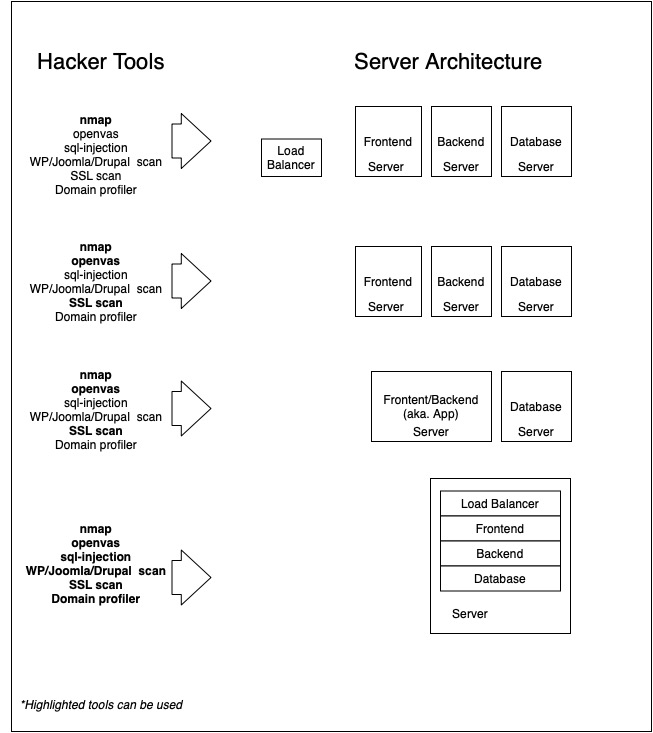
4. Logging all access and 100% monitoring
Collect your logs on central servers by observing continuous updates and time synchronization. Activate the netconsole feature on your Linux servers and provide your logs to an isolated environment by only giving write access. (In the chart above, the LOG server is in the most secure network.)
5.Inventory Management (Software hardware and version tracking)
When we use the word “inventory,” we usually think only of hardware. That is a deadly mistake that happens a lot. You should follow the versions of the hardware you use and have a lifecycle on the software you manage. There are many devices that you can use for software patches and patch followers. If you do not use any software, I recommend you use Ralph 3 open-source software.
6.Penetration testing
I advise you to test your security process professionally at least once a year. Penetration tests will help you see the weaknesses and strengths of your process. The frequency of tests does not have to be yearly; depending on your workflow, you can adopt more frequent penetration tests. The important thing is to make tests before annually updating the security document. This way, you can add the corrections you made to the new document.
It is essential to get support for social engineering and professional terms from the company that you will buy penetration tests from. You know the processes in your company, and you might not question the truths. A third eye would be asking you the right questions about this subject.
7. Email groups and security news (mail-list and subscriptions)
Follow up on the security vulnerabilities of the software you use and track them strictly. There are blog sites prepared for security by CVE and MS. By subscribing to them for free, you can quickly solve this issue. Additionally, by having good relations with the ERP company you are using, get constant information about new security updates. Some websites related to security which you can benefit from are:
8.Corporate Security Document
An IT manager should create a “Corporate Security Document” tailored to the company’s needs, utilizing the “IT Cyber Security Policy” as a reference. The Cyber Security Policy outlines the technology and information assets that require protection, identifies potential threats to those assets, and specifies the responsibilities and privileges of users. This document also includes procedures for responding to incidents that may compromise the security of the company’s computer systems and network.
As a result, following the eight points outlined above will help to ensure the cybersecurity of your systems. For more information, we recommend consulting with experts or institutions that have experience in managing IT infrastructure holistically. If you are looking for such assistance, please refer to this article on how Kubedo can help you manage your systems or contact our experienced SRE teams.


